Revamp your battle!
Brew with the new kids in the block against INFECTION

Silver lining in the battle!
Revision Hips are a devil’s work. Infected revisions are even worse.
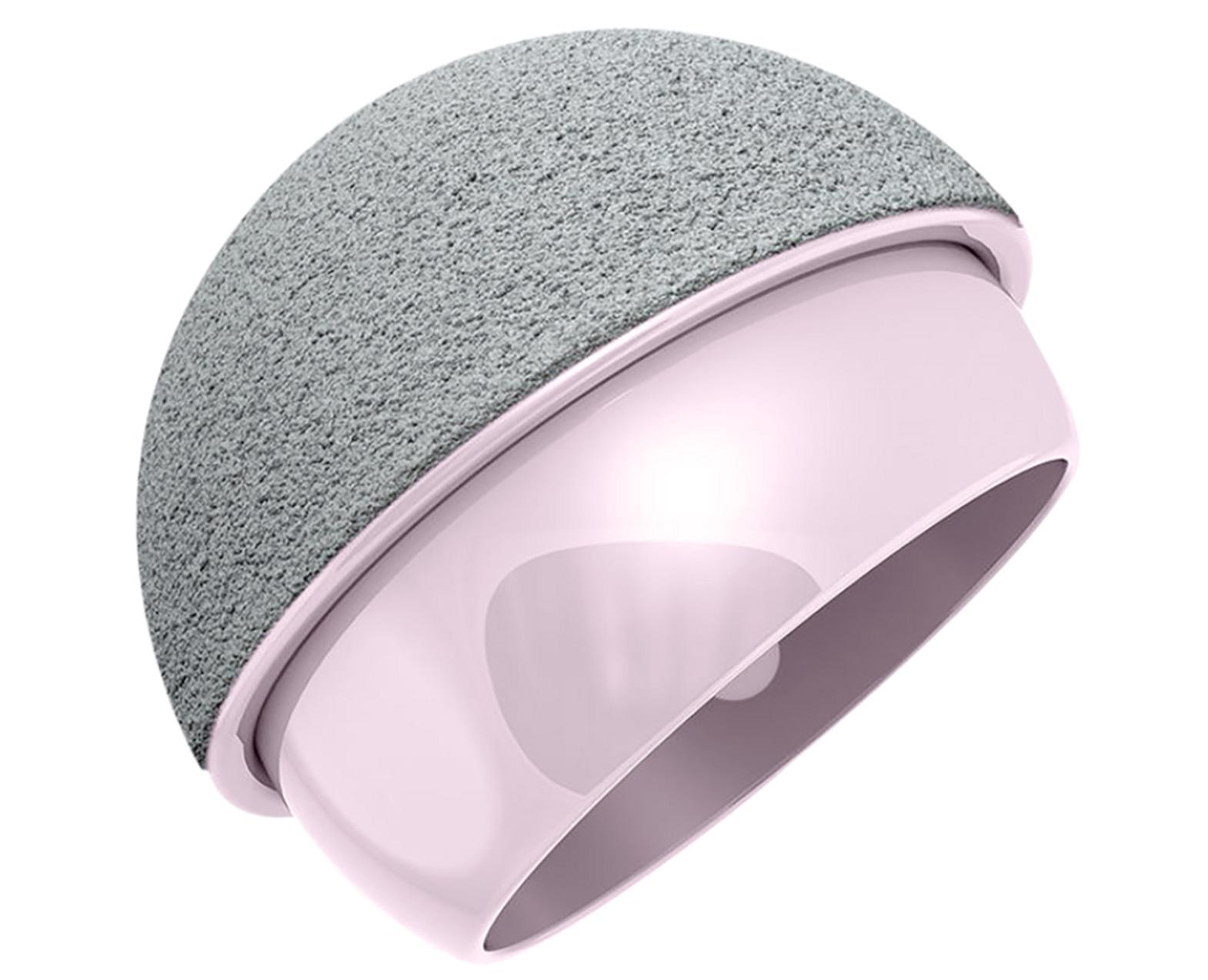
Does having a good bone-cement-implant interface that can retaliate further infection sound like a miracle? OSSIS would like to say hello. They have partnered with ‘Bio-Gate’ to develop HyProtect Antimicrobial Plasma coating. This is interesting because silver is embedded via vapor deposition between layers of siloxane and doesn’t come into contact with the bone while diffusing into the region over 90 days. This avoids the issues with bone healing.
OSSIS already has well-performing customized acetabular cups covering up to pelvic dissociations. HyProtect would possibly be an excellent breakthrough to fight the biofilm. We are quite early here as animal studies have shown good results with bone healing. Further research is ongoing.
Biofilm Breakers

Of all the bacterial strains that cause bone and joint infections, the ones that form the biofilms have raised their defense against the conventional antibiotics thereby posing a significant threat to surgeons. But it will not be the case anymore with the advent of Phage Therapy for bone and joint infections.

Image courtesy: ST Abedon et al.
Phage therapy is being heavily tested for its efficacy and practical utility in day-to-day clinical practice and the results are more than just promising. Morris et al. in their study investigated the antibacterial activity of tailored bacteriophage cocktail against biofilm-associated S. aureus and found that the treatment immediately inhibited the growth of S. aureus by >98% in eight-hour cultures. Viable bacterial numbers within biofilms on titanium surfaces were significantly reduced after exposure to the Phage cocktail, in vitro. It is only a matter of time before this modality evolves into a conventional method of management of resistant joint infections.
Newer double agents! - Latest markers of infection
Synovial D-Lactate
More than 2% of patients undergoing arthroplasty experience PJI, which is the culprit in the failure of total knee arthroplasty, hence the hunt for markers to identify them early to prevent revision has always been on and the latest one on the list is Synovial fluid D-lactate (SDL).
D-lactate is produced entirely by bacteria in the human body, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and fungi, which are specific metabolites of pathogens and can be detected in body fluids and used in the diagnosis of infection.
Z Li et al. in their recent meta-analysis showed that SDL has a sensitivity of 82% and specificity of 76% to diagnose PJI. The diagnostic odds of SDL for PJI were 14.18 (95% CI 6.17–32.58). Hence, SDL would top the list of infection panels in the coming days.
The crusade against culture-negatives!
Culture negative infections are a big nuisance.
Many add on investigations have come in the past
Microbial cell-free DNA sequencing. The cherry on the top is that it can be detected in the peripheral blood. Adriana et al found that when clubbed to routine culture, it increases the diagnostic value to 94 percent.
Game Plan post-fasciotomy
In an analysis of 370 patients, Rogers et al reported infection as many as 16.8% of patients. The most prevalent culprit post-fasciotomy was Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Combination therapies of beta-lactams, carbapenems, or quinolones with the possible addition of aminoglycosides in high-risk groups are the keystone for a win.
This antibiotic coverage should be strongly considered for routine peri‑operative prophylaxis following emergency decompression for acute compartment syndrome.

How long to wait? - Clinical titbits
Steroid injection is the most common rescue measure used when conservative treatment in a disc disease fails.
These are however close allies of infection.
Kazarian et al in their review found that Corticosteroid injection <1 month prior to lumbar spine surgery is a significant risk factor for infection.
So the waiting period is ONE MONTH.

Check these cool events that line up
The answer to the last issue Query is here
What is the critical cut-off cast index (CI) that predicts failure of conservative management of pediatric forearm fractures?
Well, the wait is over, > 0.81 it is.

The CI is a simple reliable radiographic measurement to predict the redisplacement of forearm fractures in children. A plaster with a CI of > 0.81 is prone to redisplacement and should be avoided when molding casts in distal forearm fractures. Disclaimer: The cut-off does not hold well for proximal forearm fracture.