Become a hero treating the little heroes
Welcome to the update on kids-ortho

❓Delicate implant for Delicate curves! #NeoArmory:
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis or AIS (to keep the word count low), can sometimes be a difficult conversation to have. Either brace for 16 hours a day or surgery to fuse the spine is not something that you want to discuss with kids and teenagers.
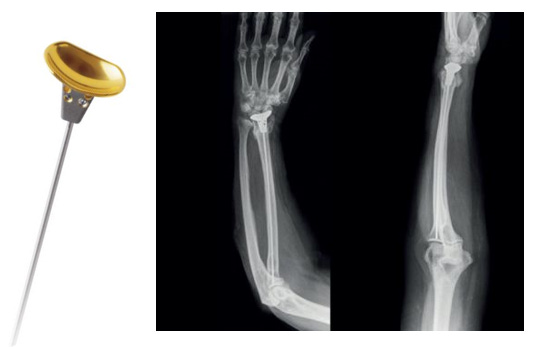
That’s where APiFix® comes in. This is a non-fusing, expandable and motion preserving option aimed at achieving correction. The system consists of self-adjusting rods which can only expand, allowing motion on the operated segments. The system acts as an internal brace and avoids permanent fusion. Implanted on the concave side via posterior approach.

A Study suggests that, at 2+ years follow up, there is 46% major curve correction with 82% patients having Cobb angle below 3 0degrees. Two polyaxial joint with ceramic coating gives it a good wear resistance lasting 10 million cycles at 700N. It also preserves 100% axial rotation, 82% lateral bending.

Sounds interesting? Now for the caveats. This was FDA approved Humanitarian use Device meaning, you don’t have to know the efficacy to market the device. This study (Level IV) shows 50% patients requiring revision and all of them showing metallosis. The study was terminated due to high complication rate. Now read the title again. The pun was always intended.
The Procedure video is here for you to check out.
A hero saving the world! #FromTheHistory:
“No masks or caps, but these heroes are saving the world. They may be too humble to call themselves heroes, but there’s no better way to describe them”
That’s how Bill Gates described Dr. Mathew Varghese in Gates Notes in 2018. For the uninitiated, Dr. Mathew Varghese runs India’s only Polio ward at the St. Stephens Hospital, New Delhi, in addition to running one of the world’s largest club foot clinics.
Completing his MBBS and Masters in Orthopaedic Surgery from the Prestigious Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, he has specialized in trauma care with particular emphasis on reconstructive surgery for trauma and deformities in adult and pediatric patients. He is the co-author of the book ‘When someone is hurt’ a first aid guide that has been translated into five languages, and ‘Prehospital Trauma Care Systems’ published by the WHO. He is also an associate faculty at the Transportation Research and Injury Prevention Programme, A WHO collaborating center at the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
In 1996, he received the Award of Honour for Reconstructive Surgery in Polio Patients, the National Award for excellence in Medicine by the T.P. Jhunjunwala Foundation for the year 2004-2005, and also the Distinguished Alumnus Award in the year 2007.
Closed reduction technique for displaced radial neck fractures #Surgical pearl:
-
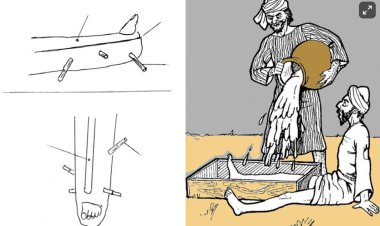
Under general anesthesia and fluoroscopic control, the limb was in elbow extension and full supination.
-
Identify the degree of forearm rotation was identified to localize maximum angular displacement.
-
In this position, longitudinal traction was applied to the forearm with varus stress at the elbow joint to distract the lateral side of the joint.
-
The pressure was applied with the thumb over the displaced radial head fragment.
-
With this maneuver, we were able to obtain a partial reduction of the radial head.
-
The elbow was pronated and flexed simultaneously with sustained pressure over the radial head to obtain further correction.
-
The reduction was then checked in a full range of flexion and extension, keeping the forearm in a mid-prone position.
-
Extremity immobilized in the mid-prone position and 90° elbow flexion.
Shah et al reduced 10 consecutive fractures with an average angulation of 77 degrees with this technique and obtained an anatomical reduction in all cases without hardware. Check out the illustrated technique video here
Kocher as Bomb squad - #MostCited:
Time-bomb is the closest analog to pediatric septic arthritis. To differentiate between septic hip and less severe transient synovitis, the four original Kocher criteria (fever, inability to bear weight, elevated serum white blood cell count, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate) were utilized. Caird added the fifth sign - elevated C-reactive protein, modifying the original Kocher criteria.
Bisht et al. analyzed the predictive value of these criteria to pick up septic knees. 96 hips and 59 knees were identified. 60/96 (62.5%) of hips and 44/59 (74.6%) of knees had septic arthritis. For hips, 5/5 criteria produced a 100% positive predictive value for septic arthritis. For knees, the combination of inability to bear weight and elevated C-reactive protein had a positive predictive value of 89.7%.
The strongest predictor for the septic knee was the refusal to bear weight (odds ratio = 14.5, p < 0.0001)

VR is a good distraction - #InTrials:
Ann E Richey et al evaluated VR as a distraction tool for decreasing fear, anxiety, and pain in pediatric patients undergoing common orthopaedic OPD procedures. Patients requiring cast or pin removals were randomized to the VR group or to the control group.
Results have shown that patients in the VR group reported significantly lower average fear scores ( P <0.001) and anxiety scores ( P =0.003) as compared with controls. Overall, patients and caregivers in the VR group reported high satisfaction scores, with 97% of patients and 95% of caregivers recommending this intervention to others.
Check out the cool events:
-
58th Annual Meeting of Scoliosis Research Society Seattle, US - 6-9 September 2023
-
2023 AOA Annual Scientific Meeting: Rural surgery – build it and they will come - Melbourne Convention and Exhibition Centre , VIC - 12 Nov - 16 Nov 2023
-
The 67th Annual Congress of the Korean Orthopaedic Association - Incheon, Seoul, KR - 12-14 October, 2023
Answer to the previous month’s question:
A patient with Pronator Syndrome presents with positive Tinel sign in the proximal anterior forearm but no Tinel sign at wrist and resists elbow flexion with forearm in supination. He also has sensory disturbances over the distribution of palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve
Where is the level of compression?
a)compression at bicipital aponeurosis
b)compression at two heads of pronator teres
c)compression at FDS fibrous arch
Answer:
Compression at bicipital aponeurosis
Question of the month:
Does ultrasound-guided popliteal-sciatic nerve block have superior pain control compared to local surgical site infiltration in pediatric foot and ankle surgery?
Want to know the answer? wait for our next issue.
Have a joyous June ahead!